Blog #1 • Read time: 3–5 min
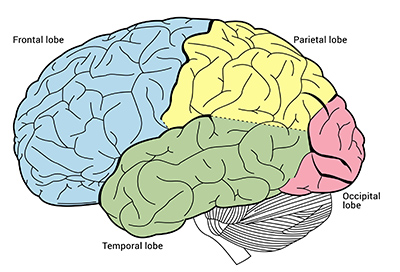
Meet the four major lobes of the cerebrum—frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital—and discover how they work together in everyday life. From planning and self-control to touch, language, hearing, and vision, each lobe contributes unique abilities. Learn simple examples you can notice in action, like solving a puzzle, recognizing a song, or catching a ball. This Blog builds a friendly map of the brain so later articles feel easier and more familiar.
Read Blog →
Blog #2 • Read time: 3–5 min
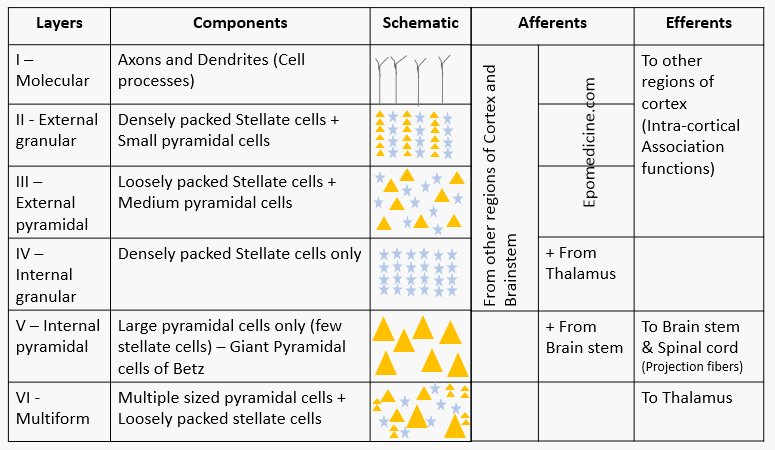
The cerebral cortex is the brain’s wrinkled outer sheet, rich with specialized areas for sensing, moving, and thinking. This guide introduces its layered structure and explains how signals flow across sensory, motor, and association regions to support perception, memory, attention, and decision-making. We’ll connect these ideas to daily experiences—reading a sentence, playing an instrument, or focusing in class—so the cortex becomes less mysterious and more like a practical toolkit your brain uses every day.
Read Blog →
Blog #3 • Read time: 3–5 min
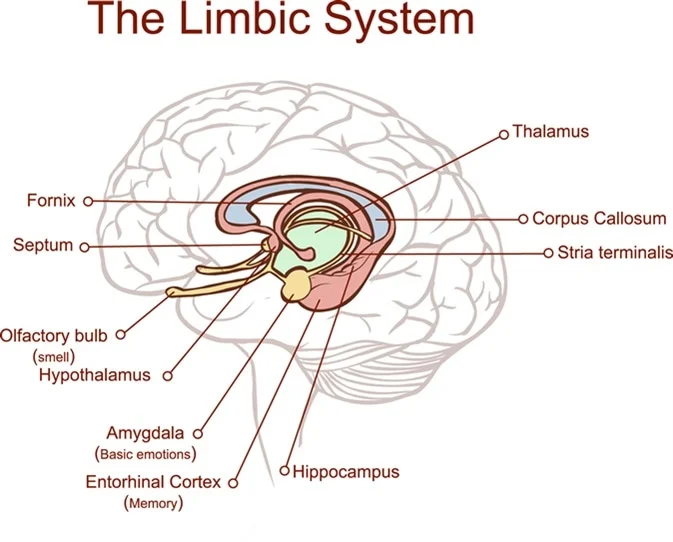
Explore the limbic system, a network that helps shape emotion, memory, and motivation. Meet key players such as the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus, and see how they interact when you form new memories, react to fear, or keep the body in balance. We’ll use real-life examples—like remembering a birthday or calming nerves before a presentation—to show how feelings and recollections are connected, while also clearing up common myths about “emotional” brain centers.
Read Blog →
Blog #4 • Read time: 3–5 min
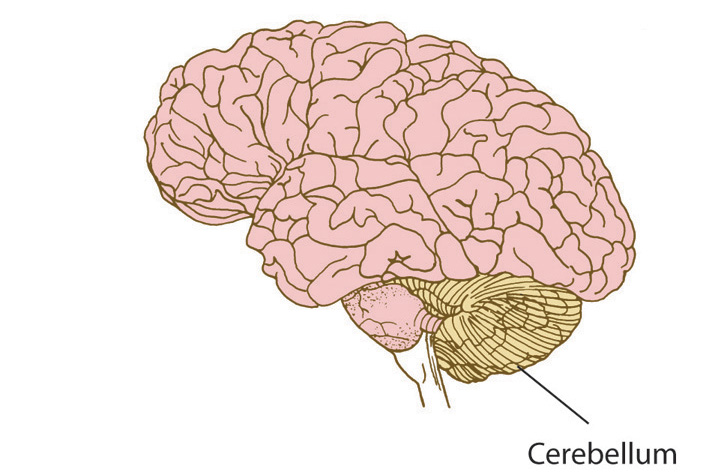
The cerebellum quietly polishes your movements, helping you stay balanced, coordinate both sides of the body, and learn new motor skills. In this Blog, we explain how it compares your intended action with what actually happens, then fine-tunes future attempts. From riding a bicycle to playing piano, the cerebellum improves timing and precision through practice. You’ll learn simple ways to notice its work in daily activities and why repetition strengthens smooth, reliable performance.
Read Blog →
Blog #5 • Read time: 3–5 min
The brainstem—midbrain, pons, and medulla—handles vital, automatic functions that keep you alive: breathing, heart rate, swallowing, and sleep-wake cycles. It also routes information between the brain and body, supports reflexes like blinking, and helps maintain Blogure. This overview shows how basic life support systems run in the background while you study, walk, or daydream. Understanding the brainstem underscores why helmet safety and medical care after head injuries are so important.
Read Blog →
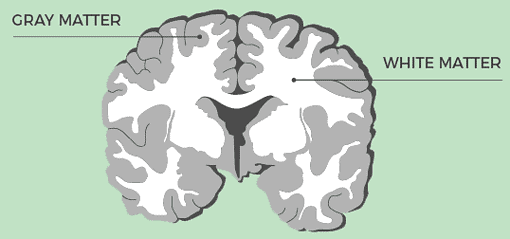
Blog #6 • Read time: 3–5 min
What’s the difference between grey and white matter? Grey matter contains neuron cell bodies that process information, while white matter bundles myelinated axons that speed signals along long routes. Together, they form efficient circuits for thinking, sensing, and moving. This Blog explains where each type is found, how development and learning shape them, and why sleep, exercise, and healthy habits support brain connectivity. You’ll gain a clearer picture of the brain’s internal wiring.
Read Blog →
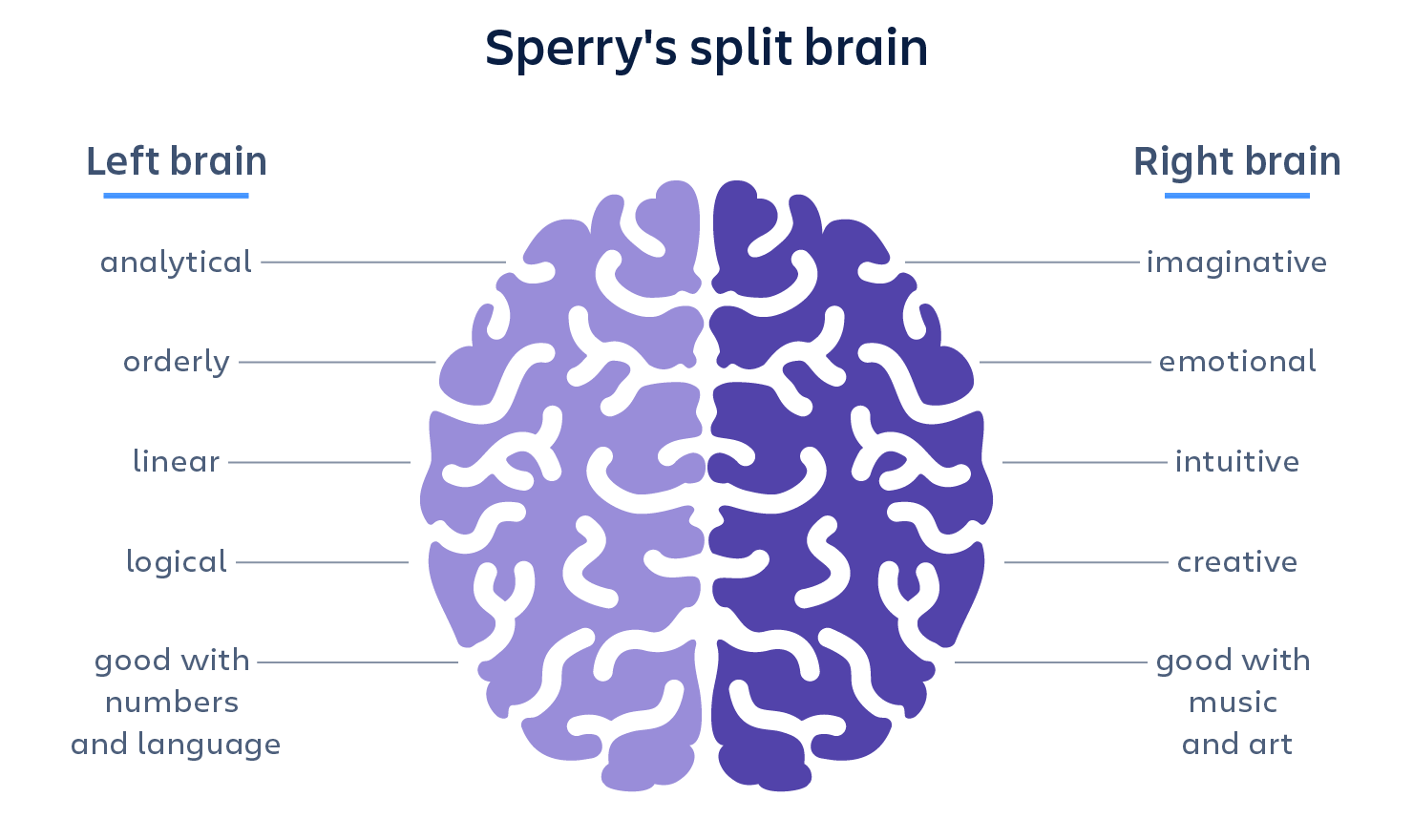
Blog #7 • Read time: 3–5 min
You’ve heard people say they’re “left-brained” or “right-brained.” Reality is more nuanced. While some functions show lateralization—language is often more left-dominant, and aspects of spatial attention lean right—both hemispheres constantly collaborate through the corpus callosum. This article separates useful facts from catchy myths, highlighting how teamwork across hemispheres supports creativity, logic, language, and problem-solving. You’ll leave with a balanced view of brain specialization and why labels can be misleading.
Read Blog →
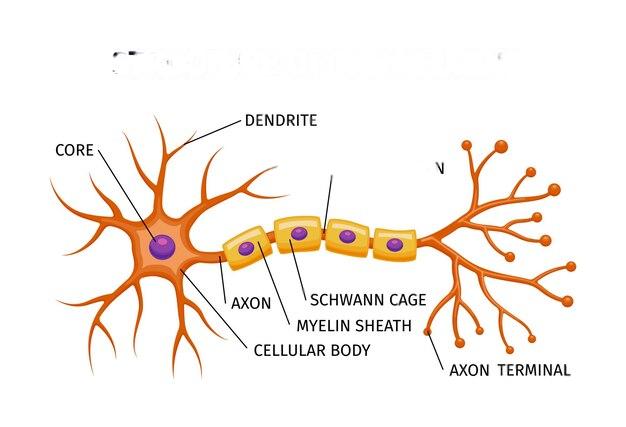
Blog #8 • Read time: 3–5 min
Neurons are communication specialists. Each cell receives signals through dendrites, processes them in the soma, and sends spikes along the axon to synapses, where chemical messengers bridge tiny gaps to the next neuron. This primer explains action potentials, neurotransmitters, and how synapses strengthen or weaken with experience—foundations for learning and memory. We’ll use everyday analogies to make complex processes clearer, helping you picture how thoughts, movements, and feelings emerge from coordinated neural activity.
Read Blog →
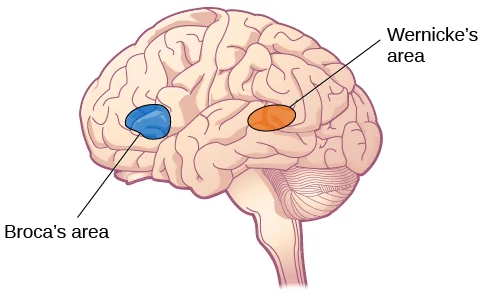
Blog #9 • Read time: 3–5 min
Broca’s area (frontal lobe) helps plan and produce speech, while Wernicke’s area (temporal lobe) supports understanding words and sentences. This Blog explains classic observations from aphasia—when injuries disrupt expression or comprehension—and updates the story with modern insights: language relies on a broader network, including pathways like the arcuate fasciculus. You’ll see how reading, speaking, and listening coordinate across regions and why bilingual experience can shape brain organization in flexible ways.
Read Blog →
Blog #10 • Read time: 3–5 min
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change with experience—strengthening useful connections, forming new routes, and pruning others. It supports learning new skills, adapting after challenges, and refining abilities across the lifespan. Here, we connect plasticity to practice, feedback, and rest, showing why spaced repetition and quality sleep matter. You’ll learn encouraging, realistic ways to nurture a growth mindset while appreciating that change is gradual, guided by healthy habits and consistent effort.
Read Blog →









